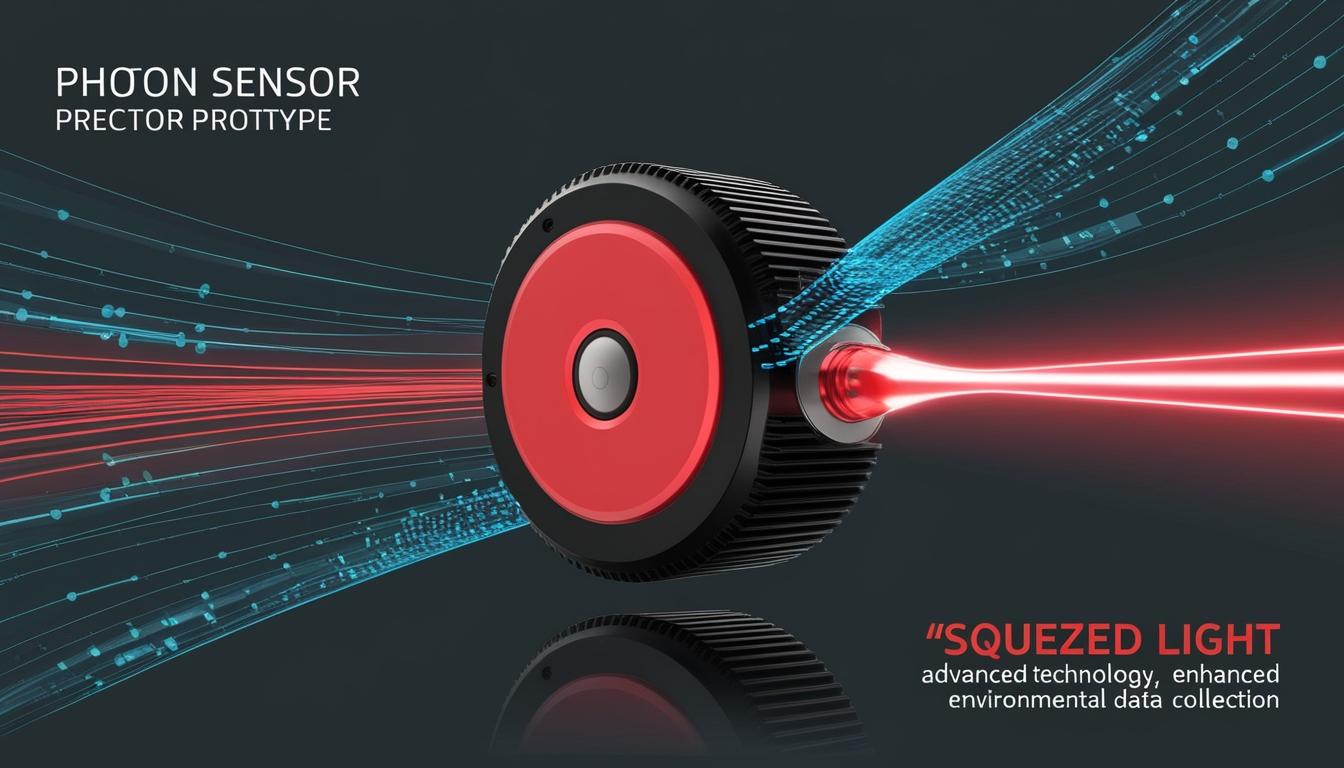
The Electronics Weekly Blog reports on a significant advancement in the realm of photonic sensors being developed as part of DARPA’s INSPIRED (Intensity Squeezed Photonic Integration with Revolutionary Detection) programme. The initiative is spearheaded by BBN Technologies, a subsidiary of RTX, which is seeking to push the boundaries of sensor precision beyond the conventional limitations imposed by shot noise.
Shot noise, which arises from the quantum nature of light, places restrictions on the sensitivity of traditional sensors, effectively capping their performance. To overcome this challenge, BBN Technologies is leveraging the quantum properties associated with light, specifically through the use of a custom-designed prototype that requires a detection sensitivity 16 dB below this fundamental shot noise limit. This new development aims to enhance environmental data collection, promising precision greater than ten times that of current sensor technologies.
Dr. Mo Soltani, principal investigator at BBN, elucidates the potential impact of this technology, stating, “Light is a powerful tool that finds widespread use in sensors like LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) for mapping, autonomous navigation, and more.” He elaborates on the constraints that current sensors face, noting, “Today’s sensors are limited by the randomness inherent in the way light fluctuates.” This random fluctuation leads to variations in the number of photons detected, even when the light source maintains stability.
To address this issue, the concept of “squeezed light” is introduced. Dr. Michael Grace, a quantum information scientist at BBN involved in the project, explains the mechanism behind this innovation: “Our device minimizes the photon noise by ‘squeezing’ the light source — suppressing certain kinds of quantum fluctuations while augmenting others.” This technique enables the extraction of information from specific photonic properties without being restricted by shot noise.
The collaborative efforts of BBN are set to combine expertise from various locations, including Cambridge, Massachusetts; San Diego, California; College Park, Maryland; and Toronto, Canada. In addition to its internal team, BBN is partnering with quantum and photonic experts from Xanadu Quantum and the University of Maryland, with contributions from Raytheon’s Advanced Technology business.
RTX, under which BBN Technologies operates, also has its fingers in another innovative project involving wireless power beaming technology. Recently, Raytheon secured a contract with the U.S. Army to develop directed energy capabilities aimed at distributing power on the battlefield. This initiative, overseen by the U.S. Department of Defense’s Operational Energy Strategy, seeks to enhance logistics and maintain the safety of troop locations. Under this contract, Raytheon is working to create advanced wireless power transmission and reception systems to meet the demands of both manned and unmanned military operations.
As these advancements in sensor technology and wireless power distribution progress, they stand to influence a broad spectrum of applications ranging from navigation to logistical support in military operations, highlighting the potential and versatility of emerging technologies in modern business practices.
Source: Noah Wire Services