The evolution of agriculture in response to global population growth and changing demographics has led to significant transformations in food production practices, particularly in livestock farming. Urban Farm Online reports that an influx of individuals moving due to conflicts, economic opportunities, and environmental factors has necessitated a rethink of food supply systems, especially in regions like Europe and North America that are welcoming diverse populations. This demographic shift is impacting the food market, mandating adjustments to meet varied dietary preferences and cultural practices.
Traditional farming methods, which have long been celebrated for their ecological advantages, are increasingly inadequate to satisfy the growing demand for food. Large corporations dominate the livestock and poultry industries, offering mass-produced products to retail chains and supermarkets, effectively sidelining smaller, local producers. The transition towards industrialised farming methods has been primarily driven by technology, with numerous advancements facilitating the scale and efficiency of meat production.
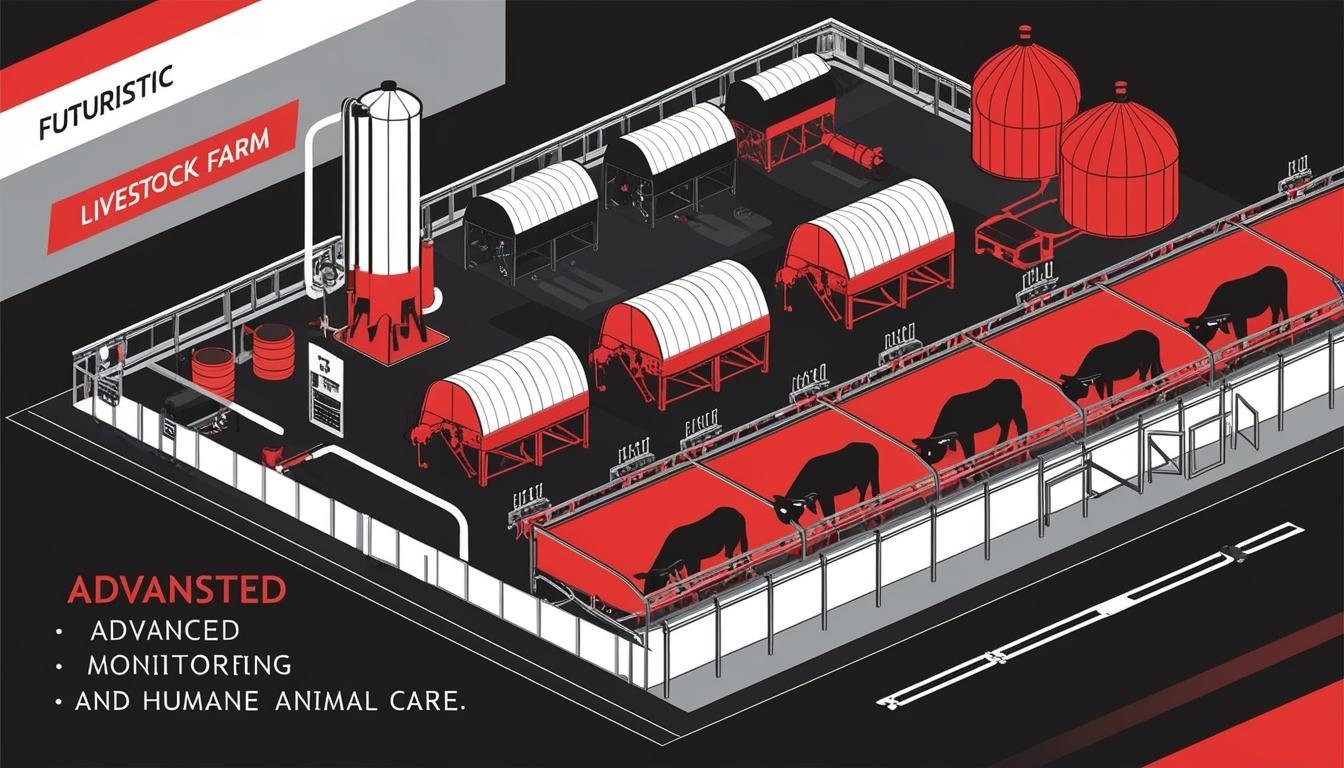
Among the innovations shaping modern livestock farming are advanced remote monitoring systems that ensure optimal conditions within animal housing. The facilities for cattle and poultry have been transformed into what can be likened to medical environments, where cleanliness and health standards are rigorously upheld. Automation plays a crucial role in maintaining these standards, with cameras providing 24/7 oversight of both livestock and facilities, allowing for immediate responses to any irregularities.
Ventilation within farming structures has also benefitted from technological improvements. Modern air conditioning systems continuously regulate temperature and humidity, creating ideal living conditions for animals. Advances in equipment, such as the invention of hypocycloid gear motors, have further enhanced airflow management. The flooring used in animal housing has also been tailored for specific needs, additionally supporting the overall climate control.
Drones have emerged as another tool in agricultural technology, particularly in the supervision of livestock. These unmanned aerial vehicles monitor herds while they graze, helping farmers observe animal behaviour and health status in real-time. Such surveillance is critical to maintaining herd welfare, as it allows farmers to identify problems quickly.
The introduction of electric fencing technology has revolutionised pasture management. This innovation not only enhances the safety of livestock but also prevents them from grazing on unauthorised land, which could lead to detrimental environmental impact.
Milking processes have become increasingly automated, with new machinery capable of simultaneously milking multiple animals while recording individual health and production data. This technology ensures that the quality of milk is tracked from an individual animal's output to its health history.
The poultry industry, too, has seen technological advancements, notably in the development of sophisticated incubators that closely monitor environmental conditions essential for hatching. The improvements in these systems allow for controlled and optimal conditions that support the healthy development of chicks.
A focus on individual animal health has also led to the use of pedometers and urine detection systems on farms. These technologies enable farmers to track the activity levels and dietary health of livestock, identifying any issues related to weight and nutrition. Monitoring urine composition aids in understanding the environmental impact of livestock and can inform better management practices to promote both animal welfare and ecological sustainability.
Overall, the integration of technology into livestock farming practices has reached a high level of sophistication. As outlined by Urban Farm Online, these advancements not only improve efficiency and production but also ensure that animals are treated with greater care. The increasing awareness around humane treatment and biodiversity in agriculture underscores the broader implications of these developments, reflecting a commitment to both ethical standards and sustainable practices as part of the global food chain.
Source: Noah Wire Services